Healthcare has traditionally relied on in-person consultations. Doctors, nurses, and other health professionals typically see patients at clinics, hospitals, or medical offices. Face-to-face interactions have long been considered essential for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care. However, advances in digital technology—ranging from computers to smartphones and wearable devices—have revolutionized the way healthcare is delivered. Today, patients and providers can connect virtually, and medical care is no longer confined to a physical location.
This shift is driven by telehealth, a technology-enabled approach that is transforming the healthcare landscape. By allowing medical professionals to interact with patients remotely, telehealth is making healthcare more accessible, convenient, and efficient.
Read More: Unlock the Life-Changing Benefits of Telehealth: Why It’s the Smart Choice for Your Health
What is Telehealth?
Telehealth refers to the delivery of healthcare services at a distance using digital technologies. It encompasses a wide range of applications, from conducting virtual consultations and monitoring patient health remotely to providing education and training for medical professionals. While telemedicine focuses specifically on delivering medical care at a distance, telehealth has a broader scope. It includes preventive care, mental health counseling, patient education, and ongoing professional development for healthcare providers.
In practical terms, telehealth allows doctors to assess symptoms, provide prescriptions, and guide treatment plans without the need for an in-person visit. Patients can have consultations via video calls, receive updates on their health status through apps, and even use wearable devices that transmit vital data to their care team in real time.
The Benefits of Telehealth
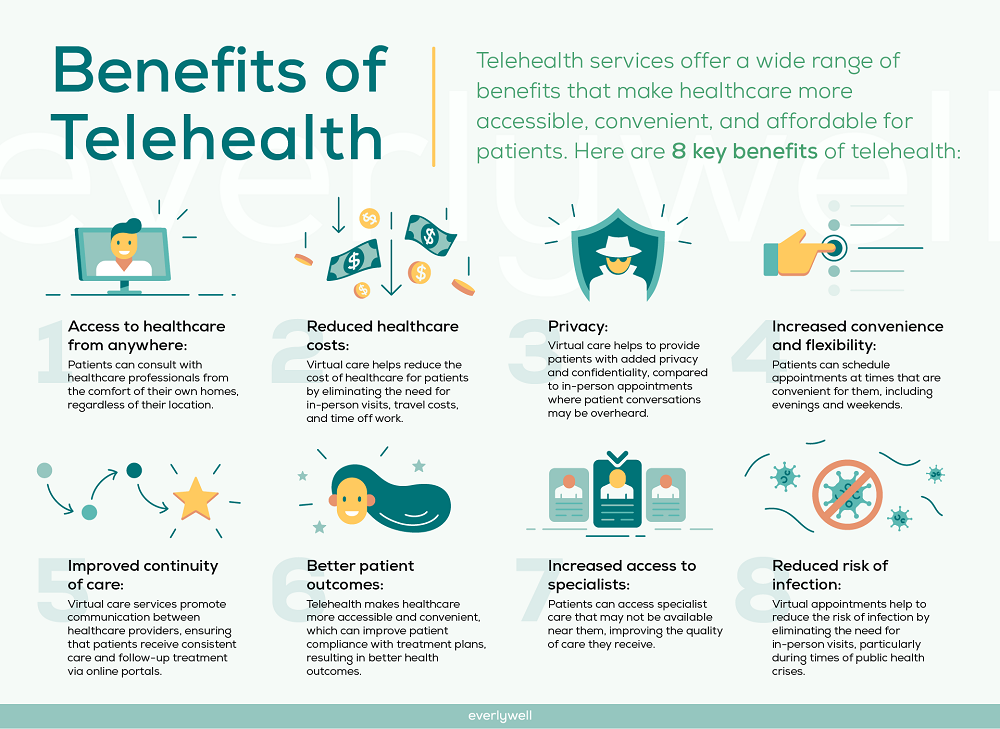
Telehealth offers a multitude of advantages, making it a game-changer in modern healthcare. Some of the most significant benefits include:
Improved Accessibility
For patients living in rural or underserved areas, accessing healthcare has always been a challenge. Telehealth bridges this gap by connecting patients to specialists and general practitioners without the need for long-distance travel. This convenience ensures that more people receive timely medical care, reducing the risk of untreated conditions worsening over time.
Convenience and Flexibility
Telehealth allows patients to schedule appointments at times that suit them, avoiding long waits in crowded clinics. This flexibility also extends to healthcare providers, who can manage their schedules more efficiently and see more patients without compromising quality. For patients with mobility issues, chronic illnesses, or busy schedules, telehealth can significantly reduce stress and logistical challenges.
Cost-Effectiveness
Remote consultations can reduce healthcare costs for both patients and providers. Patients save on travel expenses, parking fees, and time off work, while providers can optimize operational costs by reducing the need for physical office space and staff. Over time, telehealth may contribute to overall cost savings within the healthcare system.
Enhanced Patient Engagement
Telehealth empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare. With access to digital tools and real-time monitoring, patients can track their own health metrics, communicate with their care team, and make informed decisions about their treatment. This heightened engagement can improve adherence to care plans and lead to better health outcomes.
Continuity of Care
Telehealth ensures patients maintain regular contact with their healthcare providers, even during emergencies or pandemics. Continuity of care is essential for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Remote monitoring and virtual consultations enable doctors to detect early warning signs, adjust treatments, and intervene before serious complications arise.
Challenges and Limitations of Telehealth
While telehealth offers many advantages, it also comes with certain challenges. Understanding these limitations is crucial for patients, providers, and policymakers.
Technology Barriers
Not all patients have access to reliable internet connections or modern devices. Older adults and low-income populations may struggle to use telehealth platforms effectively, which could exacerbate existing healthcare disparities. Additionally, technical glitches during virtual consultations can disrupt communication and compromise care quality.
Limited Physical Examination
Certain medical conditions require hands-on examination, laboratory tests, or imaging studies that cannot be conducted remotely. While telehealth can handle many routine assessments, it cannot fully replace in-person visits for complex diagnoses or emergency care.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Transmitting sensitive medical information over digital platforms raises privacy and security risks. Healthcare providers must implement strict encryption protocols and comply with regulatory standards to protect patient data. Patients should also be aware of potential vulnerabilities and take precautions when using telehealth services.
Regulatory and Insurance Issues
Telehealth regulations vary by region, affecting how services are delivered and reimbursed. Some insurance providers may not cover virtual consultations at the same rate as in-person visits. These legal and financial considerations can influence patient access and the widespread adoption of telehealth.
Telehealth in Practice

Telehealth applications span multiple areas of healthcare. Some of the most common use cases include:
- Primary Care Consultations: Patients can receive routine checkups, discuss symptoms, and manage prescriptions remotely.
- Mental Health Services: Virtual therapy sessions provide convenient and confidential support for individuals experiencing anxiety, depression, or stress.
- Chronic Disease Management: Remote monitoring devices track vital signs like blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate, enabling doctors to adjust treatment plans in real time.
- Postoperative Follow-Ups: Patients can report recovery progress and receive guidance without returning to the hospital, reducing the risk of infection and hospital congestion.
Specialist Access: Telehealth allows patients to consult specialists who may be located far away, ensuring timely diagnoses and interventions.
The Future of Telehealth
Telehealth is expected to continue evolving as technology advances and healthcare systems adapt. Emerging trends include:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: AI can assist in diagnosing conditions, predicting health risks, and personalizing treatment plans.
- Wearable Health Technology: Devices that monitor heart rate, oxygen levels, and sleep patterns are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing for continuous remote care.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: These technologies may enhance medical training and rehabilitation programs, providing immersive experiences for both providers and patients.
- Expanded Global Reach: Telehealth has the potential to connect patients with international specialists, breaking down geographical barriers to high-quality care.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is telehealth?
Telehealth is the delivery of healthcare services remotely using digital technology. It includes virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and online health education for both patients and healthcare providers.
How is telehealth different from telemedicine?
Telemedicine focuses specifically on delivering medical care remotely, such as diagnosing and treating patients. Telehealth has a broader scope, encompassing preventive care, mental health counseling, patient education, and professional training for healthcare providers.
What are the main benefits of telehealth?
Telehealth improves accessibility for patients in remote areas, offers convenience and flexible scheduling, reduces costs, enhances patient engagement, and ensures continuity of care for chronic conditions.
Are there any risks or limitations to using telehealth?
Yes. Telehealth may face technology barriers, limited ability to perform physical examinations, privacy and data security concerns, and varying insurance coverage or regulatory restrictions.
Can telehealth replace in-person medical visits?
While telehealth is effective for many routine consultations and follow-ups, it cannot fully replace in-person visits for complex diagnoses, emergency care, or procedures requiring hands-on examination.
How does telehealth help with chronic disease management?
Remote monitoring devices allow healthcare providers to track vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels. This enables timely intervention, adjustment of treatment plans, and better management of chronic conditions.
Is telehealth secure and private?
When used through secure, encrypted platforms that comply with healthcare regulations, telehealth is safe. Patients should also use trusted devices and follow privacy guidelines to protect their health information.
Conclusion
Telehealth is reshaping the way healthcare is delivered, offering unprecedented convenience, accessibility, and efficiency. By enabling remote consultations, continuous monitoring, and digital education, it empowers both patients and healthcare providers to engage more actively in the care process. While challenges like technology limitations, privacy concerns, and regulatory barriers exist, the benefits of telehealth are undeniable. As technology continues to advance, telehealth will play an increasingly vital role in modern healthcare, complementing in-person care and improving outcomes for patients worldwide. Embracing telehealth is no longer just an option—it’s essential for creating a more connected, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare system.


